In the realm of industrial cooling solutions, shell and tube air cooled chillers stand out as reliable, efficient, and versatile systems. Designed to meet the cooling demands of various industries, these chillers combine the robustness of shell and tube heat exchangers with the convenience of air-cooled technology. This article explores their working principles, key components, advantages, applications, and considerations for optimal selection.
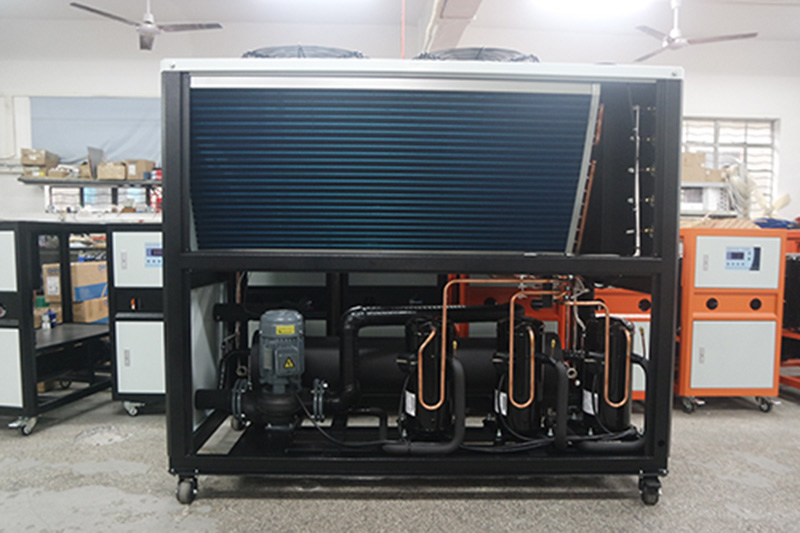

What is a Shell and Tube Air Cooled Chiller?
A shell and tube air cooled chiller is a mechanical device that removes heat from a process or space by circulating a refrigerant through a series of tubes enclosed in a shell. Unlike water-cooled chillers, these systems utilize ambient air as the cooling medium, eliminating the need for a separate cooling tower or water supply. The core components include:
How Do Shell and Tube Air Cooled Chillers Work?
The working cycle follows the vapor-compression refrigeration principle:
Key Advantages of Shell and Tube Air Cooled Chillers
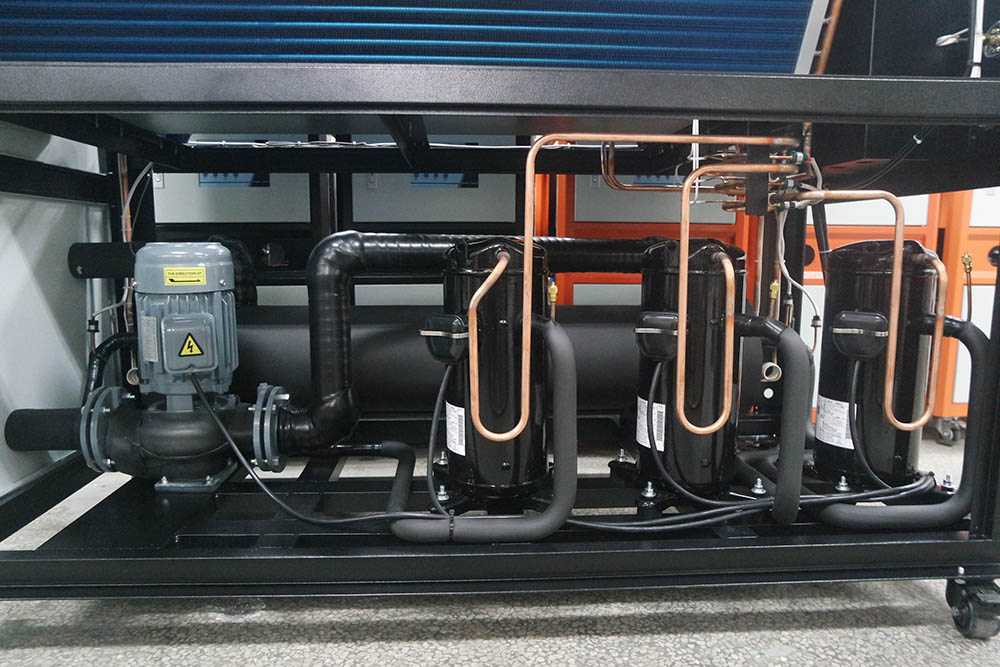
Typical Applications of Shell and Tube Air Cooled Chillers
Choosing the Right Shell and Tube Air Cooled Chiller
1. Cooling Capacity Requirements
Determine the required cooling load (in tons or kW) based on the heat generated by the process or space. Consider factors like ambient temperature, process fluid flow rate, and temperature differential.
2. Energy Efficiency Ratings
Look for chillers with high COP (Coefficient of Performance) and EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) to minimize energy costs. Modern units often feature variable speed drives for the compressor and fans, adjusting output based on demand.
3. Environmental Conditions
Evaluate the ambient air temperature, humidity, and air quality at the installation site. High dust or corrosive environments may require additional protections like stainless steel tubes or enhanced fin coatings.
4. Noise Considerations
In urban or residential areas, choose chillers with sound-dampening features such as acoustic enclosures or low-noise fans to comply with noise regulations.
5. Manufacturer Reputation and Support
Opt for reputable manufacturers who provide comprehensive technical support, detailed installation guidelines, and reliable spare parts availability.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the condenser fins to remove dust, debris, and lint that can hinder heat transfer.
Lubrication: Maintain proper lubrication of fan motors and bearings to reduce friction and wear.
Refrigerant Checks: Monitor refrigerant levels and pressure to ensure optimal performance and detect leaks early.
Electrical System Inspections: Check wiring, connections, and control panels for signs of damage or loose connections.
Conclusion
Shell and Tube Air Cooled Chillers offer a practical and efficient cooling solution for a wide range of applications, combining the benefits of robust heat exchange technology with the simplicity of air-cooled operation. By understanding their working principles, advantages, and selection criteria, businesses can make informed decisions to meet their cooling needs effectively. Whether for industrial processes, commercial HVAC, or renewable energy systems, these chillers provide reliable performance, energy efficiency, and low maintenance, making them a valuable investment for any cooling-intensive operation.
For more information on selecting the ideal shell and tube air cooled chiller for your specific requirements, contact our team of experts today.